Expansion of the Teresianas-Ganduxer school
Barcelona, Spain

Project details
Year: 2014
Surface: 2.845 m² (new construction) 644 m² (refurbishment)
State: Built
Tipology: Tertiary
Photography: Simón Garcia
More information
Industrialized work with mixed systems.
Project developed from the GREEN evaluation criteria (GBCe).
Location
Energy
label
Environmental improvement
Emissions CO2
Kg CO2/m2
Consumed energy
KWh/m2 year
General information
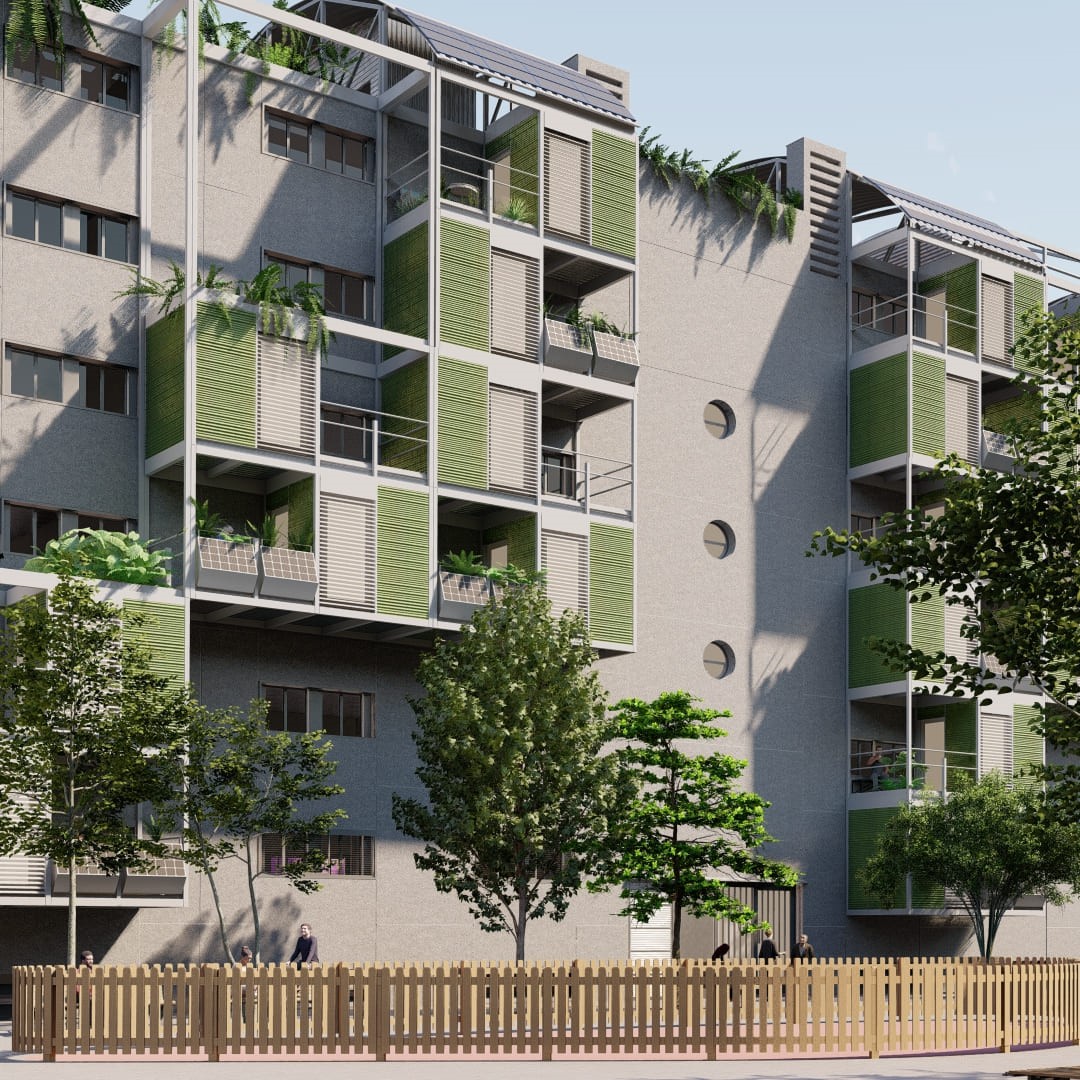
It is about the expansion of the Teresianas Concerted School on Ganduxer street in Barcelona.
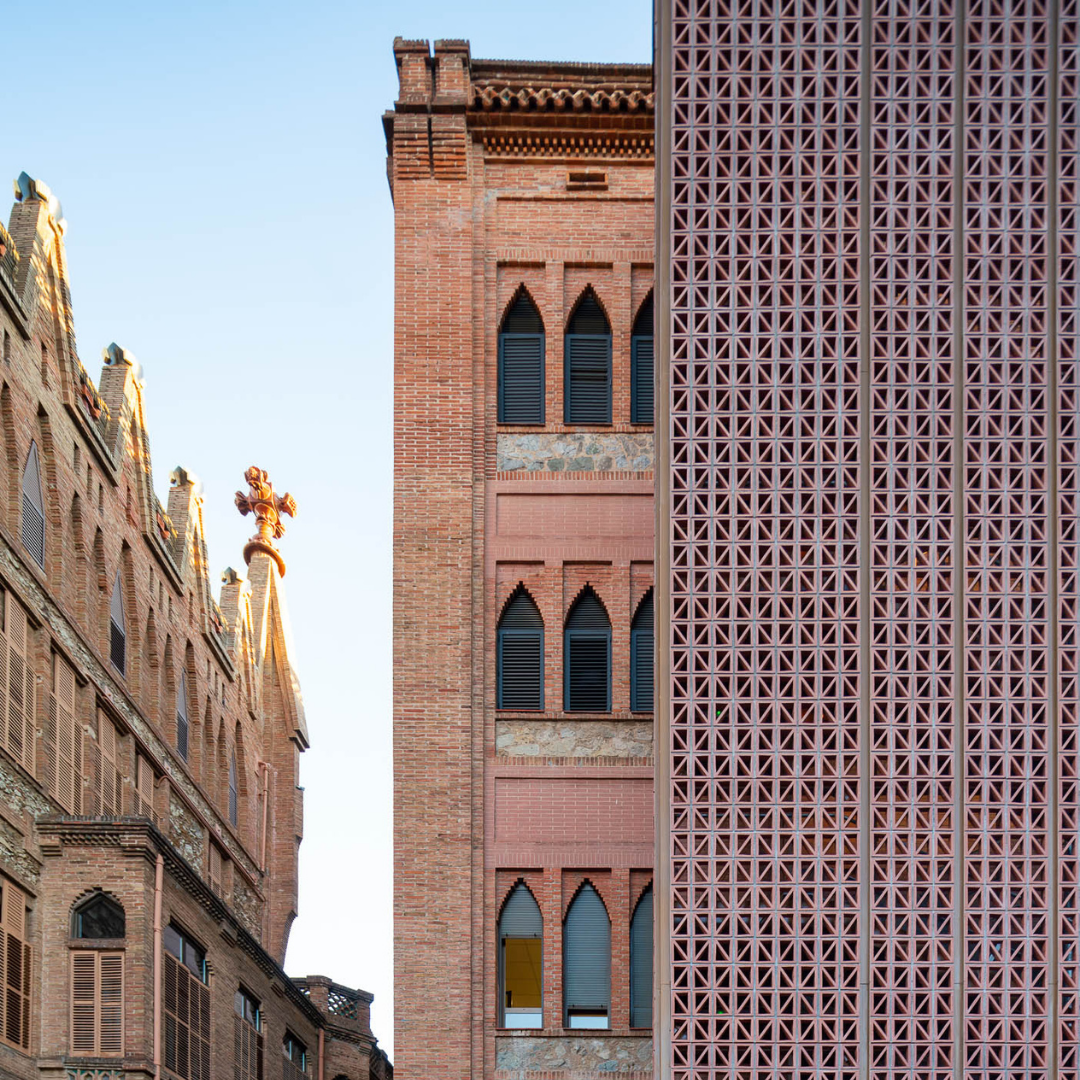
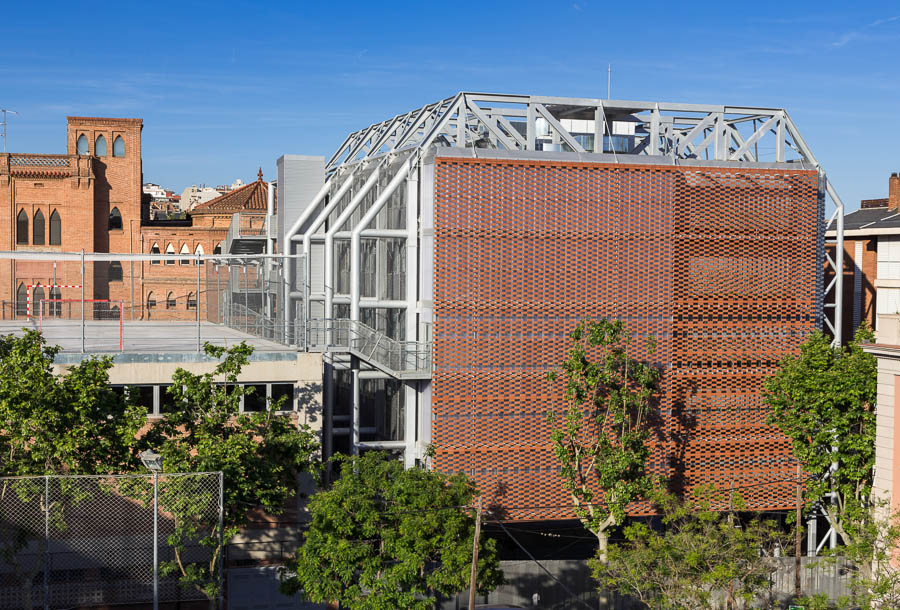
The main challenge was to propose an extension in a protected environment, where the presence of a first building designed by Antoni Gaudí flooded the complex.
Several locations of the new construction were studied and it was decided to place the extension in the most appropriate place so as not to affect the visibility of the “Gaudi Building”.
The new volume respects the height and distances of the adjoining buildings and is functionally linked to an existing sports hall.
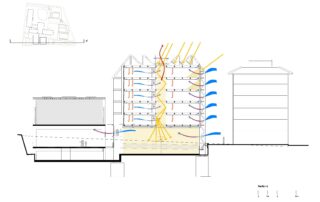
The building had to speak of its time, without turning its back on the textures of the existing building. A ceramic woven façade was chosen that works as a lattice towards the street and light and luminous elements towards the interior of the school complex. This double skin that thermally and lightly sifts the interior allows freedom and flexibility in the distribution of windows and the opaque elements that are functionally necessary.
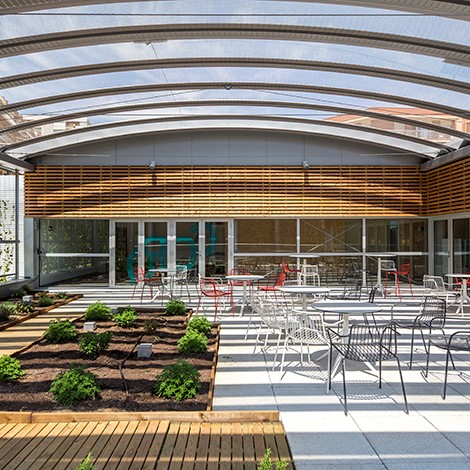
Exteriors
The location of the building makes it possible to restructure the general operation of the School and makes it possible to clearly differentiate access for second-cycle students, as well as provide extra-curricular services that do not interfere with the schedules and operation of the school and the religious community. The new expansion relocates all the Baccalaureate and ESO courses, as well as provides the school with a new covered sports space with the necessary infrastructures to be able to provide school and extra-curricular services.
A hanging metal structure was proposed that allowed the building to have a large open floor plan.
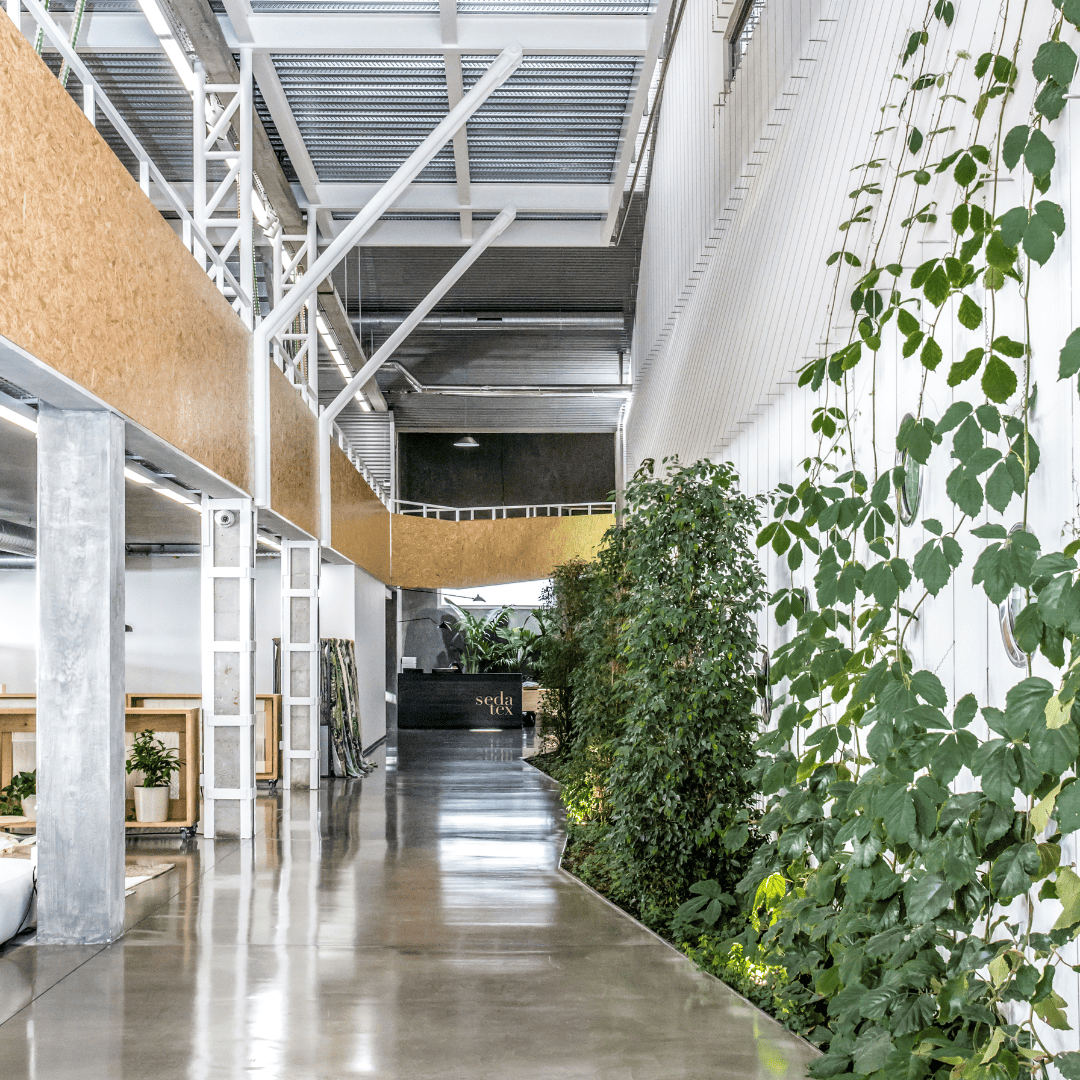
Interiors
The classrooms are distributed from a central corridor distributor that receives light, on each of the floors, through a solar chimney. The interiors are proposed from maximum austerity and simplicity, according to the strict needs of the center.
Sustainability and circular economy
The entire project was worked on to achieve the minimum consumption of air conditioning and minimum consumption of indoor air renewal. Vegetation plays an important role in air quality and cooperates with the necessary machinery to reduce pollution. Radiant air conditioning systems were chosen as a solution for greater comfort and thermal transfer.